Computing infrastructure also includes related infrastructure. This includes technologies in data centers, networks, and security. Data centers are important facilities that provide centralized computing and storage resources for AI applications. They need to have efficient data center management and maintenance capabilities. Network technology is the technology for transmitting data from one location to another, and it needs to ensure the stability and security of the network. Security technology is the technology for protecting data and systems, and it needs to ensure that data will not be leaked or attacked. Computing infrastructure is a diverse and multifaceted field, and its development and construction require the cooperation and support of all parties.
The market for AI distributed computing mainly involves three parts: computing chips (55-75%), memory (10-20%), and network equipment (10-20%). Computing chips, also known as computing chips or processing units, are chips designed specifically for performing computing tasks. Compared with traditional general-purpose chips, computing chips are optimized for specific computing tasks and have higher computing efficiency and lower energy consumption. Computing chips have a wide range of applications, including artificial intelligence, cloud computing, the Internet of Things, big data, and other fields. AI chips are also called AI accelerators or computing cards, which are modules dedicated to accelerating a large number of computing tasks in AI applications (other non-computing tasks are still handled by the CPU). From the perspective of technical architecture, computing chips are mainly divided into three categories: GPU, FPGA, and ASIC. They are the technical routes that can be commercialized on a large scale and are the main battlefield for AI chips. GPU is a relatively mature general-purpose artificial intelligence chip, while FPGA and ASIC are semi-customized and fully customized chips for the characteristics of artificial intelligence requirements. GPU is a chip optimized for computing tasks such as graphics rendering and deep learning, with the advantages of high parallelism and high efficiency. GPU is a concept first proposed by NVIDIA when it released the NVIDIA GeForce 256 graphics processing chip in August 1999. Before that, the display chip that processes image output in the computer was rarely regarded as an independent computing unit.
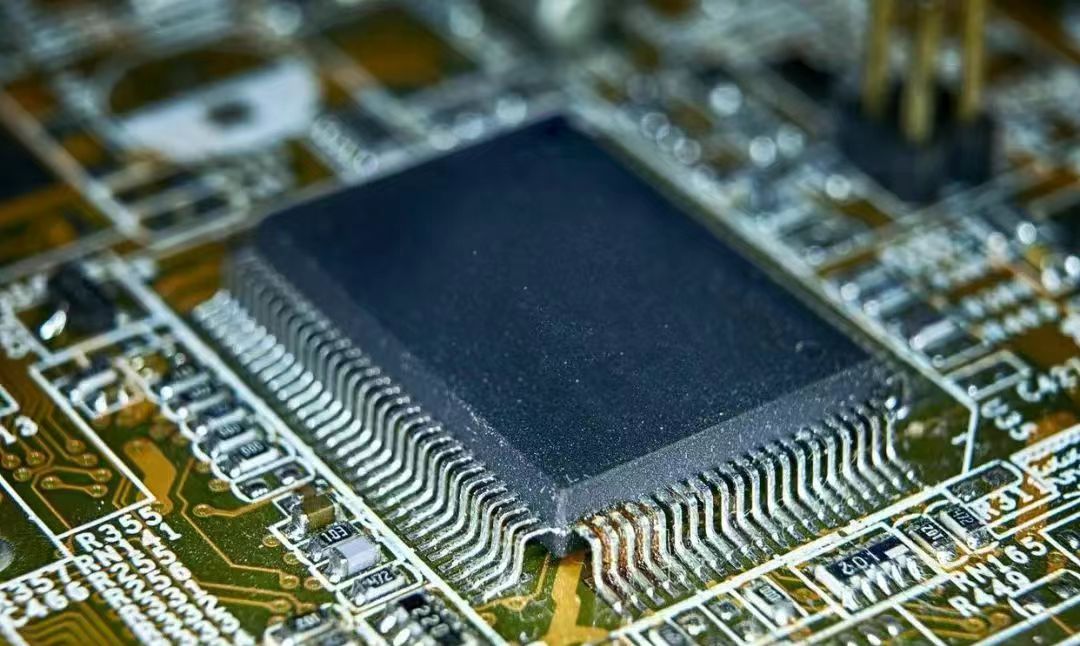
The functions of FPGA chips are not fixed after they are manufactured. Users can configure the functions of FPGA chips according to their actual needs through the dedicated EDA software provided by the FPGA chip company, thereby converting blank FPGA chips into integrated circuit chips with specific functions.
Memory chips are widely used. Servers, mobile phones, PCs and other major consumer products all have demand for memory chips, and the overall market size is huge. The industry chain of memory chips includes raw material suppliers, manufacturers, assembly and testing manufacturers, brand manufacturers and end consumers. Raw material suppliers are mainly responsible for providing basic materials such as silicon wafers and chemicals. Memory chip manufacturers are mainly responsible for the design, manufacturing and packaging and testing of memory chips. Common memory chips include DRAM, NAND flash memory chips and NOR flash memory chips.
In the server field, it can be subdivided into multiple types according to different usage scenarios, such as storage servers, cloud servers, AI servers, and edge servers.
Among them, AI servers are servers designed and optimized specifically for artificial intelligence applications. They provide powerful computing power, storage, and data processing capabilities for the development, training, and deployment of artificial intelligence applications. The upstream of the AI server industry chain is mainly raw materials, such as CPU, GPU, memory, hard disk, RAID controller, and power supply; the midstream is the server industry itself; the downstream customer groups include Internet cloud service providers, telecom operators, third-party IDC service providers, government departments, and various types of enterprises. The core components of AI servers include GPU (graphics processor), DRAM (dynamic random access memory), SSD (solid state drive) and RAID card, CPU (central processing unit), network card, PCB, high-speed interconnect chip (in-board) and heat dissipation module.