1.Definitions and characteristics of modular data centers
Modular data centers are engineered to adapt to evolving server trends—including cloud computing, virtualization, centralization, and high density—while enhancing operational efficiency, reducing energy consumption, and enabling rapid, zero-interference expansion.
Composed of self-contained units with standardized interfaces, these modules operate independently yet can be integrated to form a complete data center. They are designed to allow redundancy across compartments, ensuring reliability through mutual backup capabilities.
Characterized by integration, standardization, optimization, and intelligence, modular data centers provide a highly adaptable infrastructure and a high-availability computing environment. They are poised to address critical future needs of IT departments, such as:
*Standardization and modularization
*Virtualized design
*Dynamic IT infrastructure (resource flexibility and high utilization)
*24/7 intelligent operations management (process automation and smart monitoring)
*Business continuity support (disaster recovery and high availability)
*Shared IT services (cross-business infrastructure, information, and application sharing)
*Rapid response to changing business demands (on-demand resource allocation)
*Green data center initiatives (energy savings and carbon reduction)

2.Modular data centers solve the problems that traditional data centers face
2.1 Problems that traditional data centers face
2.1.1 Long lead time of construction
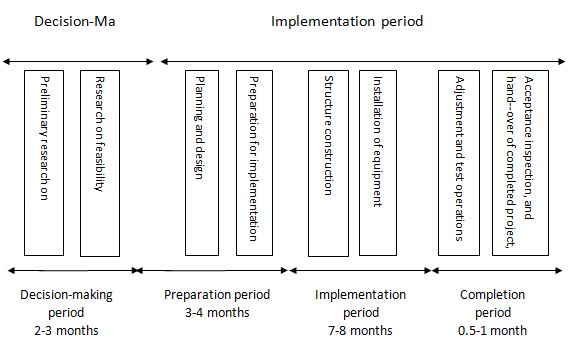
Traditional data centers are characterized by excessively long construction lead times, typically measured in years. This extended timeline stems from complex planning, design, and installation phases for infrastructure and systems. As illustrated in Figure 1, the entire process—from decision-making and preparation to implementation and completion—often requires approximately 400 days, with further delays possible.
Such a prolonged schedule is increasingly unsuitable in today's fast-paced business environment, where organizations often need to deploy new data center capacity within months, not years.
2.1.2 Poor expandability
The expandability is critical for business adaptability. Traditional data center capacity planning often faces a dilemma: it either over-provisions for uncertain future demand, leading to wasted investment, or under- provisions based only on current needs, risking business disruption and higher costs when expansion becomes necessary. This results in severe inefficiency. Studies show that the average utilization of data center infrastructure is below 50%, often as low as one-third. This underutilization represents a significant opportunity cost, locking capital that could otherwise generate returns in other projects.
2.1.3 High Energy Consumption
Traditional data centers consume excessive amounts of electricity. Their design often fails to prioritize efficient power delivery, cooling, and airflow management. Consequently, Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE) is frequently poor, typically exceeding 2.0. This inefficiency means that for every watt powering IT equipment, another watt is wasted on supporting infrastructure like cooling and power distribution.
2.1.4 Difficult Operations and Maintenance
Data center operations and maintenance are hampered by significant challenges. There is a general lack of comprehensive resource visibility and management, leading to poor service quality and chaotic processes for reporting and resolving failures. The absence of dedicated service interfaces and effective data collection methods makes it difficult for IT personnel to gather the necessary insights for system optimization.
2.2 Advantages of Modular Data Centers
2.2.1 Rapid Deployment
Modular data centers significantly shorten the planning and construction cycle. Utilizing pre-designed, factory-produced and pre-tested modules with standardized interfaces reduces on-site work. Deployment time is cut from the 7-8 months typical of traditional builds to approximately 2-3 months.
2.2.2 High expendability
The architecture allows capacity to be added in discrete phases by integrating additional modules as needed. This provides precise, on-demand scaling that optimizes initial investment and efficiently accommodates unpredictable or rapid growth.
2.2.3 Standardized and Reliable Design
Built from standardized, highly integrated modules, these data centers offer inherent stability. They can be configured to meet various redundancy levels (N, N+1, 2N), supporting reliability up to Tier 4 standards.
2.2.4 Energy Efficiency
Modular design promotes high energy efficiency. By closely matching power and cooling capacity to the actual IT load, it minimizes over-provisioning. Features like in-row cooling and cold aisle containment improve thermal management. These optimizations can achieve a PUE of less than 1.5, representing more than a 12% gain in cooling efficiency over traditional designs.
3.2.5 Intelligent Management
Integrated intelligent management systems enable granular, data-driven oversight. They facilitate multi-level energy consumption analysis, lifecycle asset management, and dynamic optimization based on analytics. This supports proactive maintenance, operational efficiency, and the implementation of energy-saving strategies.
3. Definition of Modular Products and System Components
Modular data centers can be categorized into two primary types based on the degree of prefabrication:
(1) Partially Prefabricated Data Center
This type combines prefabricated modular subsystems—such as rack, cooling, cabling, and monitoring systems—with traditional on-site construction for the remaining infrastructure.
(2) Fully Prefabricated Data Center
A fully prefabricated data center is constructed as a self-contained unit using complete, integrated modules that include power supply, racks, cooling, cabling, and monitoring. These modules are transported in sections and assembled on-site. This type still relies on external supporting infrastructure, such as generators, chillers, and power distribution systems.

4.Designing Your Modular Data Center
Modular data centers are designed as largely "set-and-forget" systems, meaning they are intended to remain stable once deployed. It is therefore crucial that the initial design aligns precisely with your use case. Below are five key considerations for planning your modular data center.
1. Modular Capacity Planning
Assess your power, cooling, and IT requirements for both initial needs and future expansion. Ensure each module can support the expected load while allowing for seamless integration of additional units as demand grows.
2. Standardized Interfaces
Adopt standardized interfaces for power, cooling, and networking across all modules. This ensures compatibility, simplifies integration and maintenance, and reduces setup complexity.
3. Cooling Systems
Choose efficient cooling solutions—such as air or liquid cooling—that match the heat output and density of your IT equipment. Design for effective airflow management and include redundancy to maintain temperature stability and prevent hotspots.
4. Power Distribution
Implement a reliable power distribution system within each module, incorporating redundancy for critical components. Design the system to handle current loads and support future expansion without major modifications.
5. Environmental Controls
Integrate monitoring and automated control systems to manage temperature, humidity, and airflow. Real-time sensors and adaptive controls help maintain optimal conditions for performance and reliability.