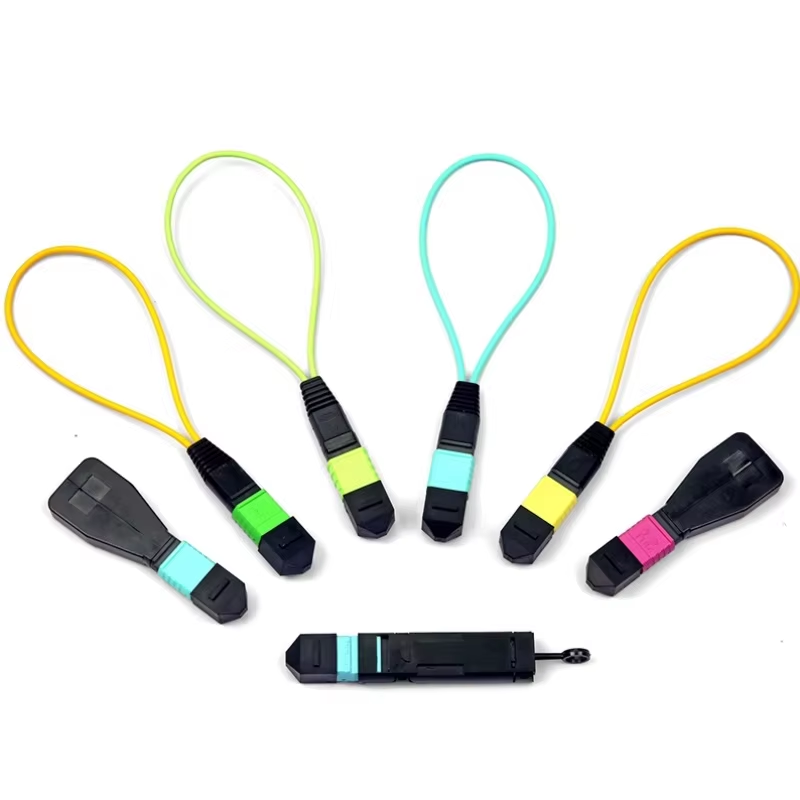
A fiber loopback cable, also known as a loopback test plug, is a fiber optic cable that routes a signal back to its source. This loopback configuration enables network engineers to check whether the transmission system is working as intended. Essentially, it’s a tool designed to verify, diagnose, or isolate issues in fiber optic networks.
These cables typically come with a connector on each end or as a plug with a built-in loop. Common connector types include SC, LC, MTP/MPO, and ST connectors, ensuring compatibility with various fiber optic systems.

Why Are Fiber Loopback Cables Important?
Fiber loopback cables serve a critical role in maintaining the integrity of fiber optic networks. Here’s why they’re indispensable tools for IT professionals and network managers:
Simplified Testing and Diagnostics
With a fiber loopback cable, you can immediately verify whether the input/output ports, network receivers, and transmitters are functioning correctly. This process reduces the time needed for troubleshooting and ensures quicker resolution of network issues.
Cost and Time Efficiency
Fiber optic networks, with all their benefits, come with intricate and sensitive components. Instead of conducting time-consuming end-to-end diagnostics, engineers can narrow down errors to a specific port or device using a loopback cable, saving time and minimizing downtime.
Reduced Network Downtime
Proactive maintenance is the hallmark of an efficient IT team. Fiber loopback cables allow professionals to test and validate devices during installation or routine maintenance without causing disruptions to the broader network.
Versatility
From telecommunications to data centers, and even extending into industrial automation systems, fiber loopback cables support various use cases wherever high-speed fiber optic connectivity is involved.
Fiber Loopback Types and Configurations
Typically, fiber optic loopbacks are simplex fiber optic cables terminated with two connectors at each end, forming a loop. The black housing is used to protect the optical cable, which makes the design more compact and more robust to use. Depending on the type of fiber used, there are singlemode loopbacks and multimode loopbacks available with different polish types. According to the type of optical connector for loopback, fiber optic loopback cables can be divided into MTP/MPO, LC, SC, FC, ST & E2000, etc. When testing fiber optic transceiver modules, LC, SC, and MTP/MPO loopback cables are most commonly used.
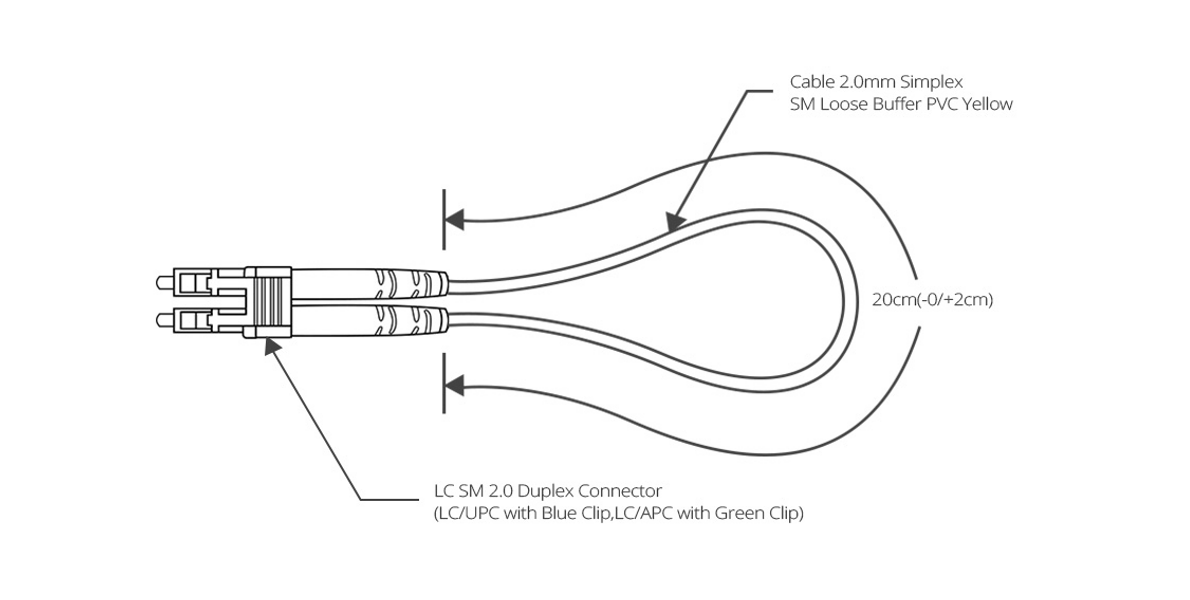
(1) LC, SC Fiber Optic Loopback
LC and SC Fiber Optic Loopbacks use simplex cables and common connectors, and understanding their configuration is not difficult. A fiber optic loopback consists of two fiber optic connectors that plug into the output and input ports of the device. Push-pull design for easy insertion and extraction for testing 10G or 40G or 100G interface transceivers. Specifically designed for troubleshooting network fault nodes.
Take the LC Fiber Optic Loopback cable as an example, is one of the most popular cables. It supports the test of transceivers featuring LC interfaces. They feature low insertion loss, low back reflection, and high-precision alignment to conform to RJ-45 style connectors.
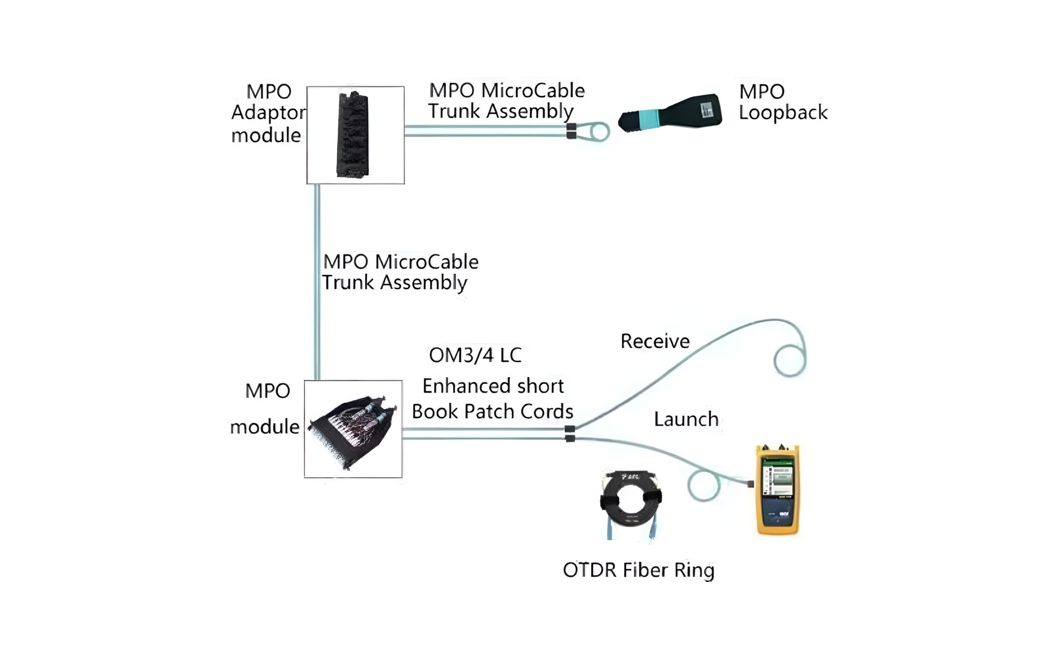
(2) MPO Fiber Optic Loopback
MPO Fiber Optic Loopback, put both ends of the optical fiber into an MPO connector, so that the optical path is in the same connector, without changing the signal or repeating the signal back to itself. It is mainly used to test parallel optical devices, which can provide an effective solution to test the transmitting ability and receiving sensitivity of network equipment. Especially in 40/100G network communication, various potential phenomena can be located through the return signal, so as to achieve effective testing and evaluation of single components or interfaces on the paired optical fiber network and the network. Since the number of fibers in different applications is not always the same, their configurations vary.
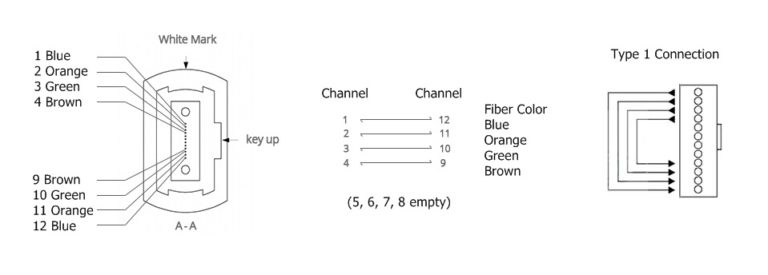
8 Core MTP/MPO Fiber Loopback Configuration
In an 8-fiber MTP/MPO loopback, eight fibers are arranged on either side of the connector, and the 8-fiber loopback polarity channels are aligned, leaving the middle four channels empty. The optical fiber adopts the straight structure of 1-12, 2-11, 5-8, 6-7. The polarity channel arrangement is shown in the figure below.
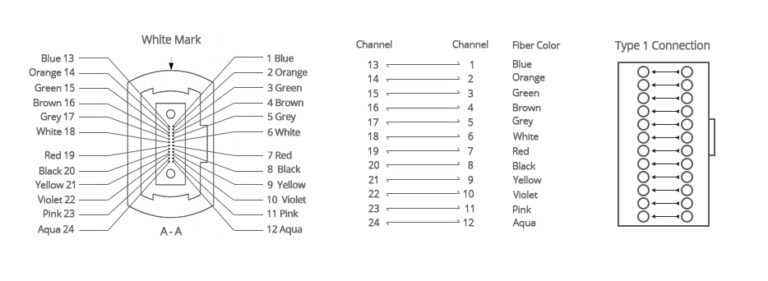
12 Core MTP/MPO Fiber Loopback Configuration
The only difference between the 12-core MTP/MPO loopback and the 8-core MTP/MPO loopback is that the central four channels are not empty. Its alignment is 1-12, 2-11, 3-10, 4-9, 5-8, 6-7.

24 Core MTP/MPO Fiber Loopback Configuration
The 24-fiber MTP loopback also adopts type 1 polarity. 24 Fiber Loopback Polarity Channel Alignment:
When Should You Use Fiber Loopback Cables?
Installation Verification: Ensure new optical ports and devices are installed correctly.
Routine Maintenance: Periodically check that devices are operating flawlessly.
Troubleshooting Faults: Quickly isolate faults in specific devices or areas of the network.
How Do You Use a Fiber Loopback Cable?
Select the Appropriate Cable: Choose one compatible with your system’s connector type and mode (singlemode or multimode).
Insert the Cable into the Port: Connect the fiber loopback cable to the device or port you want to test.
Run Diagnostic Tools: Use software or other diagnostic equipment to send signals and analyze responses.
Interpret the Results: Compare the expected output with the actual results to identify any irregularities.
Fiber Loopback Cables in Real-Life Scenarios
Data Centers
Fiber loopback cables play a key role in ensuring the seamless operation of high-bandwidth networks within data centers. Regular testing helps reduce latency and prevent downtime in sensitive environments.
Telecommunications
Telecom systems require consistent performance, especially for voice and video services. Network engineers use fiber loopbacks to ensure robust fiber optic connections and address performance bottlenecks.
Industrial Automation
With industries moving toward interconnected systems through IoT and automation, ensuring signal integrity in fiber-based communications is paramount. Fiber loopback cables help engineers test and validate these systems.